

For example, find the recursive formula of 3, 5, 7. The tools can be launched with different form pre-sets using the links - these can be. By statistically assessing how well database and query sequences match one can infer homology and transfer information to the query sequence.
#Finding sequences how to
The coefficient of \(n^2\) is half the second difference, which is 2.A geometric sequence is a list of numbers, where the next term of the sequence is found by multiplying the term by a constant, called the common ratio. Algebra 1 > Sequences > Constructing arithmetic sequences Recursive formulas for arithmetic sequences CCSS.Math: HSF.BF.A.2, HSF.LE.A.2 Google Classroom Learn how to find recursive formulas for arithmetic sequences. Sequence Similarity Searching is a method of searching sequence databases by using alignment to a query sequence. If the terms of a sequence differ by a constant. The second difference is the same so the sequence is quadratic and will contain an \(n^2\) term. We now turn to the question of finding closed formulas for particular types of sequences. Work out the \(n\) th term of the sequence 5, 11, 21, 35. In mathematics, a sequence is an ordered list of numbers or other mathematical objects that follow a particular pattern. In this example, you need to add \(1\) to \(n^2\) to match the sequence. To work out the \(n\) th term of the sequence, write out the numbers in the sequence \(n^2\) and compare this sequence with the sequence in the question. It is often useful to find a formula for a sequence of numbers. Half of 2 is 1, so the coefficient of \(n^2\) is 1. 21-110: Finding a formula for a sequence of numbers.

The UniGene cluster has links to transcript sequences for the gene from the Nucleotide and EST databases If there is no UniGene cluster for this gene and organism, perform a search in the Nucleotide database with the gene name, product name, or symbol. In this example, the second difference is 2. Click on the UniGene cluster of interest. The coefficient of \(n^2\) is always half of the second difference. mkdir finding-the-sequence-of-a-domain cd.
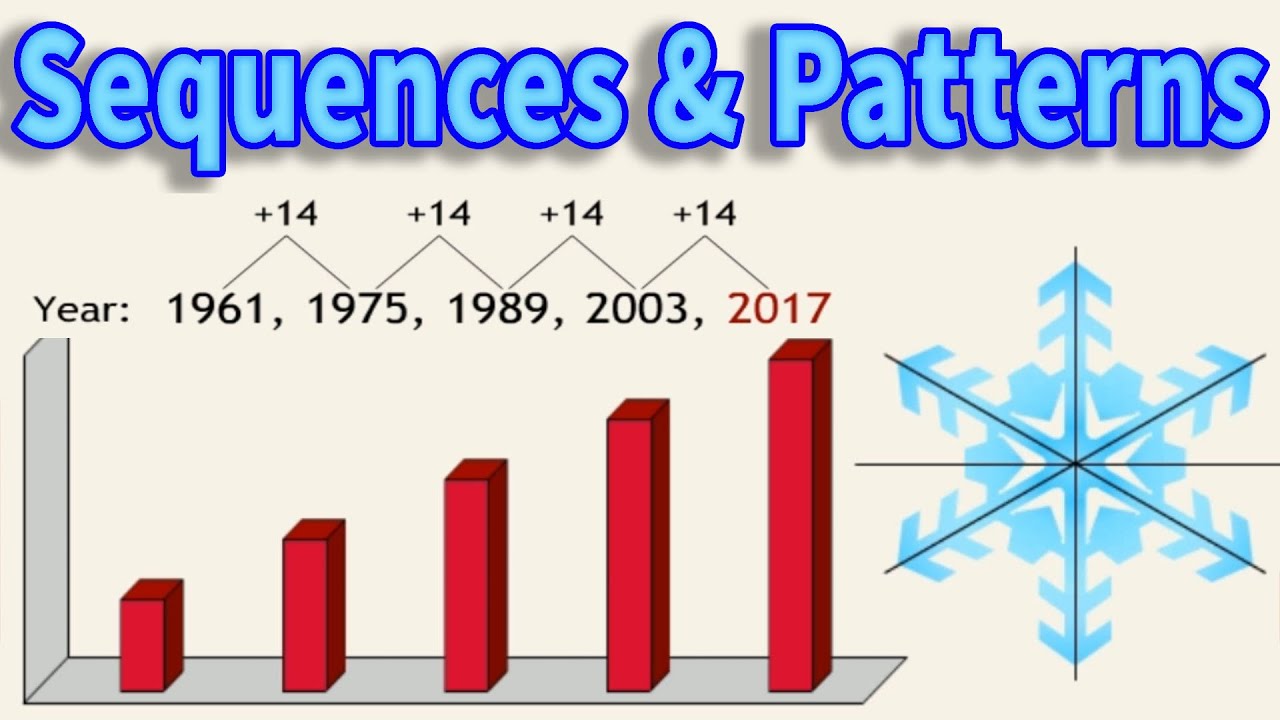
The Sequence Calculator finds the equation of the sequence and also allows you to view the next terms in the sequence. The sequence is quadratic and will contain an \(n^2\) term. To extract the sequences of domains you will first need the start and end positions. Step 1: Enter the terms of the sequence below. If the rule is to add or subtract a number each time, it is called an arithmetic sequence. The first differences are not the same, so work out the second differences. Number sequences are sets of numbers that follow a pattern or a rule. Some sequences follow a specific pattern that can be used to extend them indefinitely.

To find the 1st term, put n 1 into the formula. Work out the first differences between the terms. Sequences are ordered lists of numbers (called 'terms'), like 2,5,8. Such sequences can be expressed in terms of the nth term of the sequence. Work out the \(n\) th term of the sequence 2, 5, 10, 17, 26. This is in contrast to a geometric sequence where each term increases by dividing/multiplying some constant k. Unfortunately, finding genes in a genomic sequence (in this paper, we will only discuss genes encoding proteins) is far from being a trivial problem ( 5). They can be identified by the fact that the differences in between the terms are not equal, but the second differences between terms are equal. An arithmetic sequence is a sequence where each term increases by adding/subtracting some constant k. Quadratic sequences are sequences that include an \(n^2\) term.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
